1. Establishing a Successful, Sustainable Program Infrastructure
One of the hc1 PBM fundamentals focuses on establishing a strong program infrastructure.
For the hospital, this included establishing a clinical executive sponsor, project lead, a multidisciplinary PBM Committee, and physician stakeholders in all high blood use specialties. The health system’s PBM Committee adopted an impressively detailed charter, including oversight and responsibility for the overall program implementation plan.
2. Implementing Clinical Best Practices
The Patient Blood Management committee met in March of 2022, and the team immediately began working on implementation recommendations based on hc1’s five PBM fundamentals.
- Establish a clinically driven, multidisciplinary PBM program infrastructure.
- Develop and distribute meaningful PBM reports that reflect clinical performance at the hospital, specialty, and provider level to drive ownership and accountability.
- Implement evidence-based transfusion guidelines and effective computerized physician order entry for blood components with clinical decision support.
- Roll out ongoing, customized clinical education and awareness campaigns focused on the most significant opportunities for improvement.
- Implement clinical strategies to improve the recognition and management of anemia and minimize bleeding and blood loss through an anemia management program.
3. The Power of PBM Benchmarks and Analytics
The health system implemented hc1’s cloud-based PBM Analytics suite, capable of providing hundreds of meaningful clinical reports at the hospital, specialty, and provider level. hc1 PBM Analytics is used by hundreds of hospitals across the country to quickly identify outlier behavior, variation in practice, and opportunities for improvement based on hc1’s extensive benchmark dataset. In addition, PBM Analytics is vendor-agnostic, creating a smooth and seamless connection to its existing electronic medical record.
PBM Analytics enabled the healthcare system to perform a baseline analysis of hospital, specialty, and provider practice for several PBM performance metrics.
PBM Analytics and hc1’s benchmarks were used to set organization targets for each metric. The metrics were carefully selected by clinical experts to drive clinical transformation. Examples of three red blood cell (RBC) metrics selected by the hospital include percentage of RBC units ordered with a pre-transfusion hemoglobin <7.0 g/dL, percentage of RBC units ordered with a pre-transfusion hemoglobin >8 g/dL, and single unit RBC orders. The software will be used prospectively to generate and distribute automated reports to clinical stakeholders throughout the health system regularly to reduce avoidable transfusions.
4. Anemia Management Program
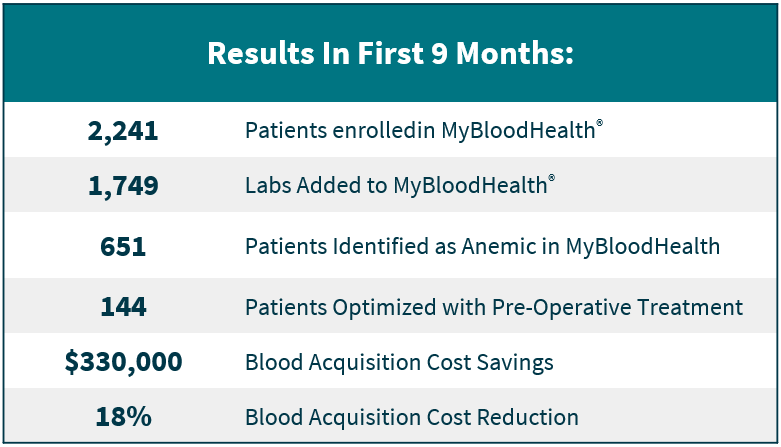
The health system implemented pre-surgical anemia management (PSAM) as part of a comprehensive PBM program by leveraging hc1’s innovative anemia management software tool, MyBloodHealth. MyBloodHealth® is an enterprise-wide software tool that supports effective and efficient implementation of pre-surgical anemia management programs. Leadership identified the pre-surgical testing (PST) department as the champion for PSAM, leveraging existing resources (five PST nurses and three mid-level providers) to support the program. Key stakeholders evaluated current and future workflows to develop best practice process improvements, including adoption of a pre-surgical anemia algorithm and anemia management reflex lab test after approval from the PBM and medical executive committee.